Presenter: Huyenlan Nguyen, DO, Elise Grgurich, DO
Dermatology Program: Lehigh Valley Health Network/PCOM
Program Director: Stephen M. Purcell, DO
Submitted on: February 29, 2016
CHIEF COMPLAINT: Left-sided facial swelling and lip swelling
CLINICAL HISTORY: A 40-year-old female with left-sided facial swelling and lip swelling. The most recent episode occurred one month ago and was associated with swelling of the face and lips. She feels the self-limited flares are related to stress and denies any associated new medications or provoking foods. She occasionally has numbness on the left side of her face that she attributes to her history of Bell’s palsy. She was treated with a course of prednisone and responded well.
PHYSICAL EXAM:
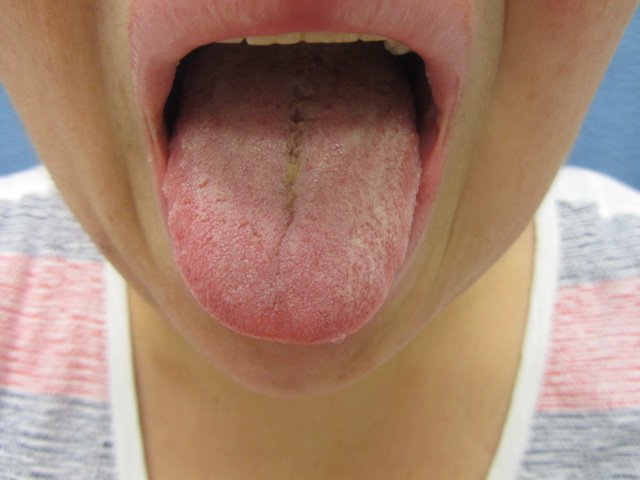
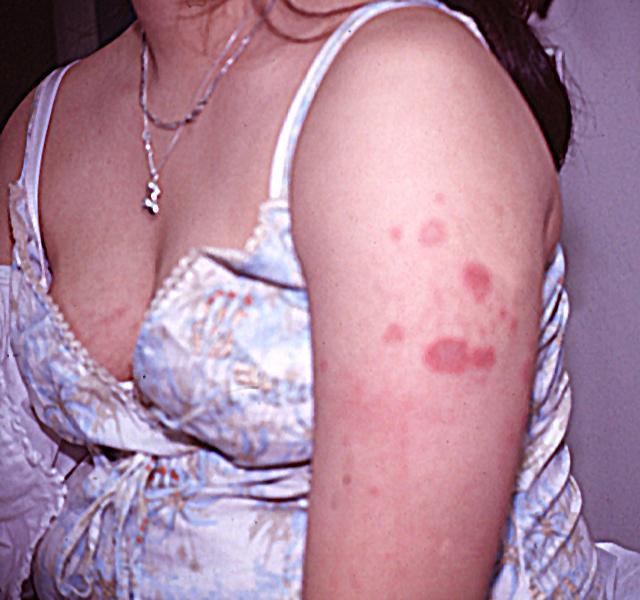
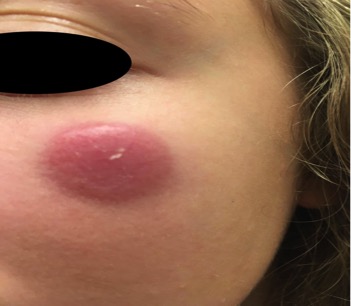
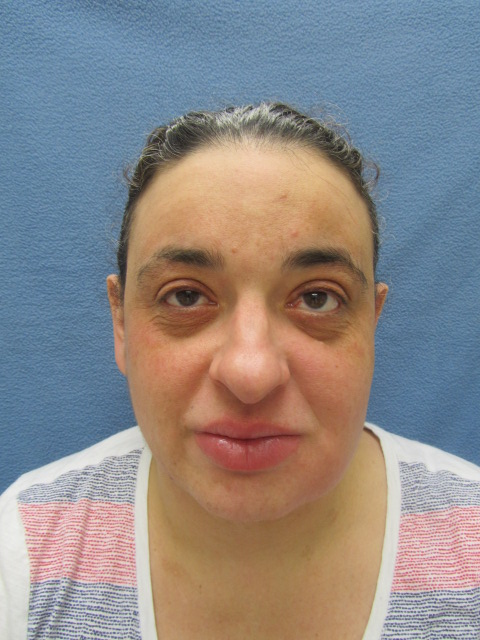
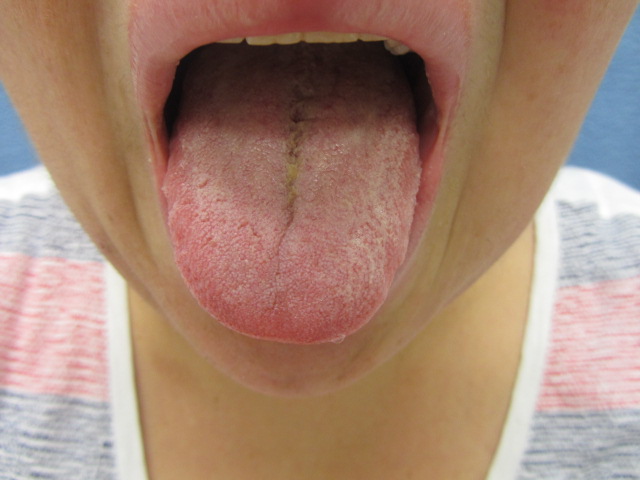
Edema of the upper and lower lips with mild scale on the lower lip. Erythema and edema of the left cheek and jawline. A few scattered erythematous papules are noted within the edematous plaque on the left cheek. The right cheek is clear.
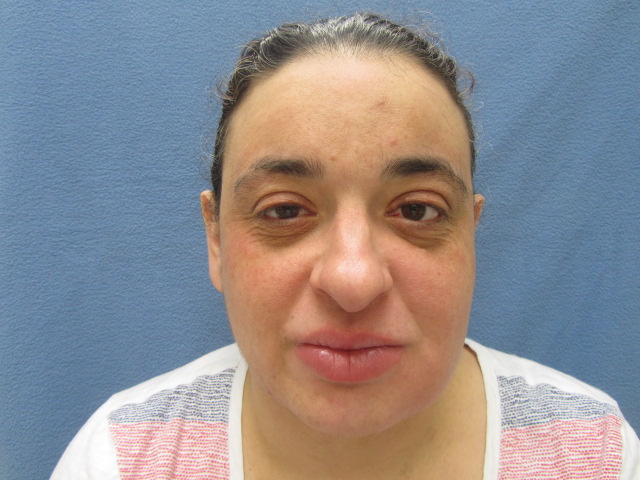
LABORATORY TESTS:
ANA screen and SSA/SSB negative, C4, C1 esterase inhibitor, ACE level, calcium level, CBC, CMP, quantiferon gold, and chest x-ray were all normal.
DERMATOHISTOPATHOLOGY:
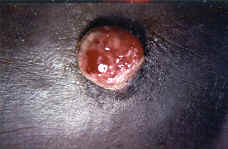
Left lower cheek, left lower lip: “Drug eruption possible. The findings are not stereotypical for any one well-defined entity. Superficial and deep periadenexal and perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate with the suggestion of granulomatous perifolliculitis.” Advanced Dermatology Associates, LTD (AD14-12537, 10/21/2014). Left lower lip: “Cheilitis granulomatosis. There is benign squamous epithelial hyperplasia with a hint of spongiosis, parakeratosis, and a superficial perivascular lymphohistiocytic infiltrate. Small collections of epithelioid histiocytes are present but rare. PAS and GMS stains are negative for fungus. These findings support the clinical impression of Melkersson-Rosenthal Syndrome.”
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS:
1. Melkersson-Rosenthal Syndrome
2. Angioedema, hereditary vs. acquired
3. Granulomatous disorders: sarcoidosis, crohn’s, TB, foreign body reaction, other infection
4. Connective tissue disease
5. Lymphoma