CORRECT DIAGNOSIS:
SAPHO Syndrome
DISCUSSION:
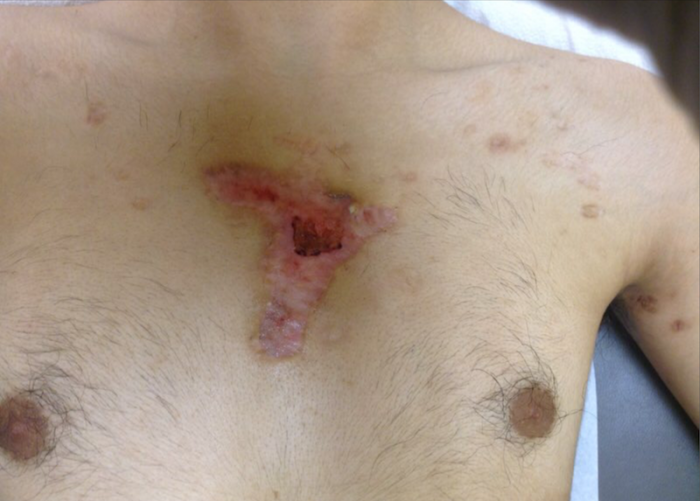
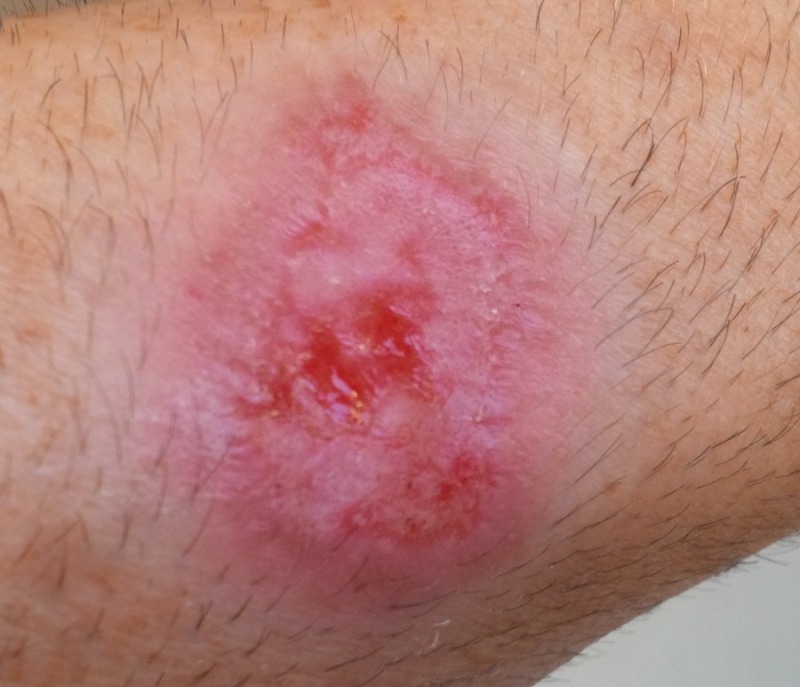
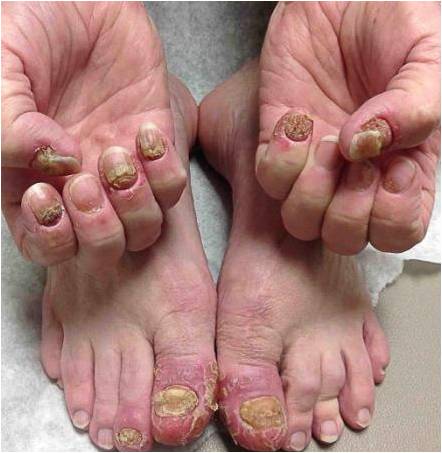
SAPHO syndrome is a disorder characterized by a combination of musculo-skeletal and dermatologic manifestations. Typically, young and middle aged adults are affected with musculo-skeletal pain, most commonly affecting anterior chest wall, synovial articulations and synchondroses, particularly the sacroiliac and sterno-clavicular joints. Skin involvement includes severe cystic acne, palmar plantar pustulosis and pustular psoriasis. Skin manifestations and osteo-articular complaints typically present within two years of each other.
Laboratory findings are usually non-specific. CRP and ESR may be elevated in some cases. HLA-B27 antigen is prevalent in as high as 30% of cases. CT and MRI radiographic findings include osteolysis, osteitis, hyperostosis and osteosclerosis. Biopsy of inflammatory infiltrates of the skin typically show non-specific inflammatory infiltrate and cultures are typically negative for bacteria.
Pathogenesis is unknown. One hypothesis suggests a link with sero-negative spondylo-arthropathies, given the high prevalence of axial involvement (i.e sacroiliitis, and asymmetric paravertebral ossifications) seen with inflammatory bowel diseases (Crohn’s and ulcerative colitis) and psoriasis.
Treatment options include NSAIDs, colchicine, corticosteroids, bisphosphonates, and disease-modifying agents, such as, methotrexate, sulfasalazine, infliximab for musculoskeletal disease. Antimicrobials, such as, azithromycin, doxycyclin, bactrim and clindamycin for skin manifestations (P. acnes and S. aureus have been isolated in some patients). Local treatments include intralesional kenalog (ILK), topical steroids, topical antimicrobials, and retinoids.
TREATMENT:
Humira and Methotrexate
REFERENCES:
Matzaroglou, C., Velissaris, D., Karageorgos, A., Marangos, M., Panagiotopoulos, E., & Karanikolas, M. (2009). SAPHO syndrome diagnosis and treatment: Report of five cases and review of the literature. Open Orthopaedics Journal, 3, 100-106. doi:10.2174/1874325000903010100
Hayem, G., Bouchaud-Chabot, A., Benali, K., et al. (1999). SAPHO syndrome: A long-term follow-up study of 120 cases. Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism, 29, 159-171. doi:10.1016/S0049-0172(99)80005-5
Olivieri, I., Padula, A., Ciancio, G., Salvarani, C., Niccoli, L., & Cantini, F. (2002). Successful treatment of SAPHO syndrome with infliximab: Report of two cases. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 61, 375-376. doi:10.1136/ard.61.4.375
Rozin, A. P., & Nahir, A. M. (2007). Is SAPHO syndrome a target for antibiotic therapy? Clinical Rheumatology, 26, 817-820. doi:10.1007/s10067-006-0450-4