CORRECT DIAGNOSIS:
Adiposis Dolorosa (Decrum’s Disease)
DISCUSSION:
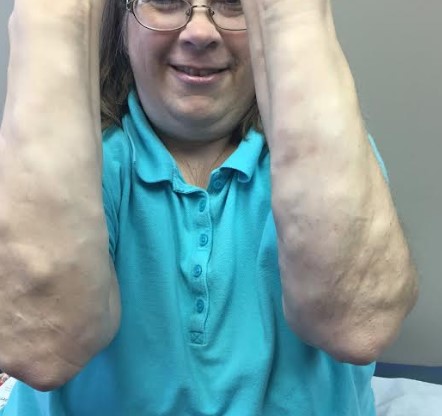
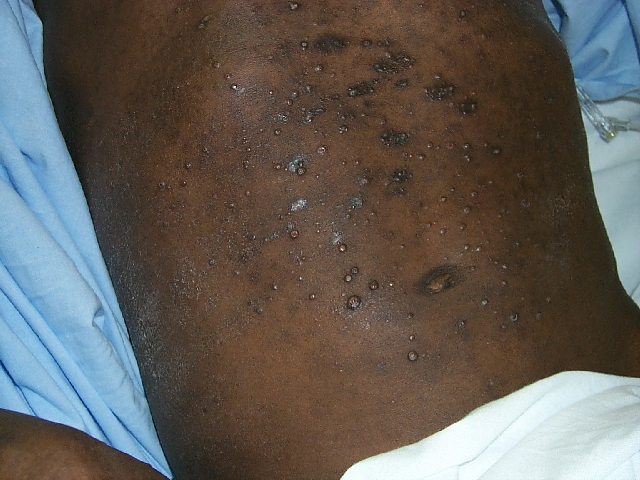
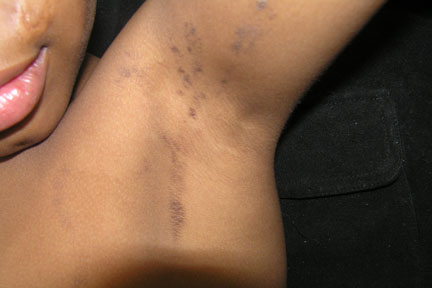
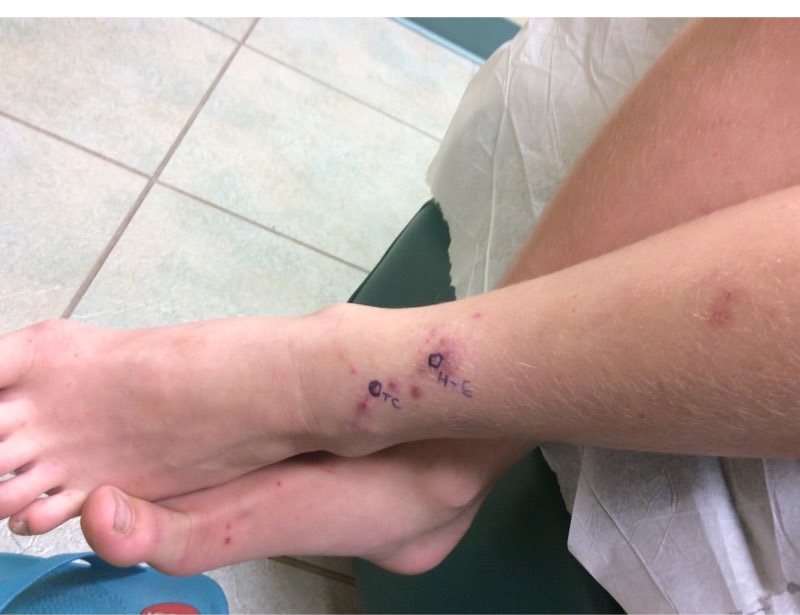
Adiposis dolorosa, also known as Dercum’s disease, primarily affects women, particularly those who are obese and postmenopausal, typically between the ages of 35 and 50. This condition is characterized by multiple painful lipomas located on the arms and trunk. Patients often experience severe, debilitating pain that occurs in periodic waves, likely due to nerve compression caused by the lipomas. The size and shape of these lipomas can vary significantly. Co-morbidities frequently associated with adiposis dolorosa include fibromyalgia, hypothyroidism, and diabetes. Additional symptoms may involve anxiety, memory issues, fatigue, sleep disorders, depression, and difficulty breathing.
Histopathological examination usually reveals findings consistent with a typical lipoma, though it may also demonstrate other pathologies, such as angiolipomas. Laboratory tests generally show negative results for inflammatory or autoimmune markers. A review from 2012 proposes a four-part classification system for the condition: Type I (generalized diffuse form with painful adipose tissue but no lipoma formation), Type II (generalized nodular form with pain in both adipose tissue and lipomas), Type III (localized nodular form with pain primarily around lipomas), and Type IV (juxtaarticular form with excess fat deposits around joints, such as the knee).
The patient in this case most likely falls under Type II: generalized nodular form. Treatment focuses on pain management, and while several treatments have been suggested, no single method has proven fully effective. A multidisciplinary approach is essential for optimal pain management. Initial treatment typically involves NSAIDs for pain relief, although these can sometimes be ineffective. Some case reports mention additional treatment options, including metformin, infliximab, methotrexate, interferon alpha-2b, and pregabalin. In cases involving interferon alpha-2b, patients may have a history of hepatitis C. Surgical options, such as liposuction and excision, may also be considered, though there is a risk of lipoma recurrence.
TREATMENT:
Our patient’s goal for treatment was to decrease irritation and pain from the angiolipomas. Since pregabalin and gabapentin were not controlling the patient’s pain completely, dronabinol 2.5mg was tried twice daily for four months. At the return visit, the patient revealed that dronabinol did not alleviate the pain, and at this visit, she also requested surgical excision treatment. We recommended off-label use of apremilast for its anti-inflammatory properties. Samples were provided for the patient at this visit, as well as a referral to plastic surgery for surgical excision of some angiolipomas. Selenium 600-800mg once daily, cimetidine 400mg BID, and Excipial™ bruising pills were also recommended due to additional anti-inflammatory properties. At the next return visit, the patient stated she did not tolerate apremilast secondary to headaches. She was started on amitriptyline 25 mg twice daily, and 0.5 mg of naltrexone once daily for one week and increasing the dose by 0.5 mg weekly until at a dose of 3 mg for more adequate pain control. The patient was seen three months later and stated her pain was well controlled at this time. She had seen plastic surgery where she had 30 angiolipomas excised from her bilateral extremities. Current pain control regimen includes naltrexone 3 mg once daily, amitriptyline 25 mg as needed and adding gabapentin 300 mg three times daily. Although she did report dizziness with gabapentin use in the past, pregabalin became too expensive. She is due for follow-up in three months.
REFERENCES:
Hausson, E., Sevnsson, H., & Brorson, H. (2012). Review of Dercum’s disease and proposal of diagnostic criteria, diagnostic methods, classification and management. Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases, 7, 23–38. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3444313/
Herbst, K. L., & Asare-Bediako, S. (2007). Adiposis Dolorosa is more than painful fat. The Endocrinologist, 17, 326–344.
Labuzek, K., Liber, S., Suchy, D., & Okopiea, B. A. (2013). A successful case of pain management using metformin in a patient with adiposis dolorosa. International Journal of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 51, 517–524. doi:10.5414/CP201878
Singal, A., Janiga, J., Bossenbroek, N., & Lim, H. (2007). Dercum’s disease (adiposis dolorosa): A report of improvement with infliximab and methotrexate. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology, 21, 717.
Gonciarz, Z., Mazur, W., Hartleb, J., et al. (1997). Interferon alfa-2b induced long-term relief of pain in two patients with adiposis dolorosa and chronic hepatitis C. Journal of Hepatology, 27, 1141.
Lange, U., Oelzner, P., & Uhlemann, C. (2008). Dercum’s disease (lipomatosis dolorosa): Successful therapy with pregabalin and manual lymphatic drainage and a current overview. Rheumatology International, 29, 17–22. doi:10.1007/s00296-008-0635-3
Wollina, U., Goldman, A., & Heinig, B. (2010). Microcannular tumescent liposuction in advanced lipedema and Dercum’s disease. G, 145, 151–159. http://lipedemaproject.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/02/2010_Wollina_Microcannular-Tumescent-Liposuction-in-Advanced-Lipedema-and-Dercums-Disease.pdf