CORRECT DIAGNOSIS:
Dermatomyositis + systemic sclerosis
DISCUSSION:
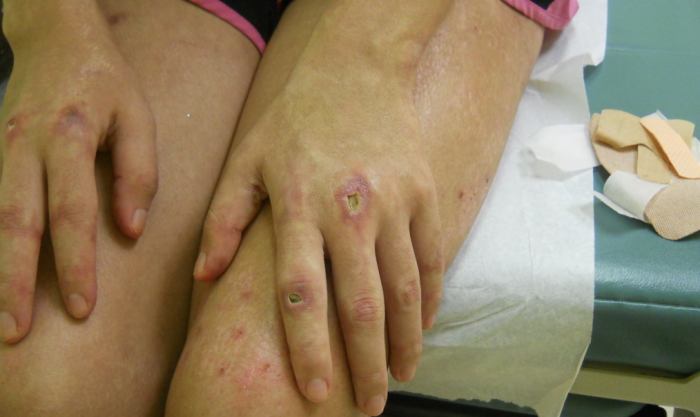
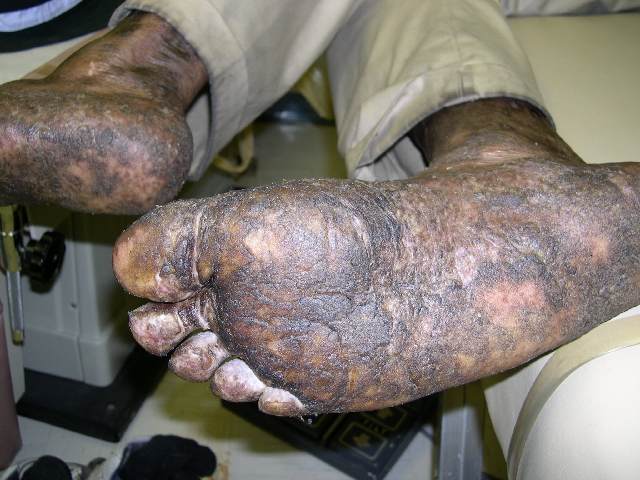
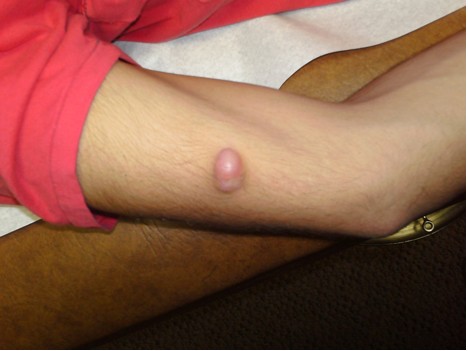
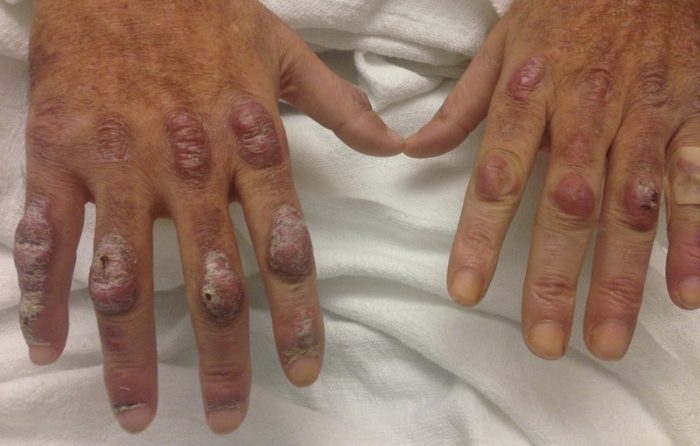
This case demonstrates findings consistent with both dermatomyositis and systemic sclerosis, which are both autoimmune connective tissue disorders that can have a wide range of clinical and serologic findings. Our patient presented with DM findings including classic rash, Gottron’s papules, proximal muscle weakness, fatigue, weight loss. She did have an unusual presentation of cutaneous ulcers over shoulders and extremities as well as digital ulcers that are less likely seen in dermatomyositis and more frequently seen in systemic sclerosis and other vasculitides. Our patient did have an initial elevated ESR, ALT/AST, and aldolase consistent with findings of DM. Interestingly enough she also had a positive anti-myeloperoxidase antibody but largely negative autoantibody panel otherwise.
In a case report by Ahmed et al, they presented a case of seronegative dermatomyositis presenting with features of anti-MDA5 subtype. The presence of vascular injury is more commonly associated with DM subtype positive for anti-MDA5 antibody. Anti-MDA5 DM is a subtype of DM Sith a characteristic mucocutaneous phenotype, exhibiting punched-out cutaneous ulcers in up to 82% of patients, with predilection for digital pulp, periungual region, MCP and interphalangeal joints, elbows, and knees
REFERENCES:
Tartar, D. M., Chung, L., & Fiorentino, D. F. (2018). Clinical significance of autoantibodies in dermatomyositis and systemic sclerosis. Clinics in Dermatology, 36, 508-524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clindermatol.2018.02.014
Narang, N. S., Casciola-Rosen, L., Shufeng, L. I., et al. (2015). Cutaneous ulceration in dermatomyositis: Association with anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 antibodies and interstitial lung disease. Arthritis Care & Research, 67, 667-672. https://doi.org/10.1002/acr.22443
Bhansing, K. J., Lammens, M., Knaapen, H. K., et al. (2014). Scleroderma-polymyositis overlap syndrome versus idiopathic polymyositis and systemic sclerosis: A descriptive study on clinical features and myopathology. Arthritis Research & Therapy, 16, R111. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar4630
Khanna, D., Hays, R. D., & Furst, D. E. (2017). Functional disability and other health-related quality-of-life domains: Points to consider for clinical trials in systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology, 56, v17-v22. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kew080
Galluccio, F., Allanore, Y., Czirjak, L., et al. (2017). Points to consider for skin ulcers in systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology, 56, v67-v71. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kew114
Cutolo, M., Smith, V., Furst, D. E., et al. (2017). Points to consider—Raynaud’s phenomenon in systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology, 56, v45-v48. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kew090
Hughes, M., & Herrick, A. L. (2017). Digital ulcers in systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology, 56, 14-25. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kew087
Iaccarino, L., Gatto, M., Bettio, S., et al. (2013). Overlap connective tissue disease syndromes. Autoimmunity Reviews, 12, 363-373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2012.07.002
Wielosz, E., Majdan, M., Dryglewska, M., et al. (2018). Overlap syndromes in systemic sclerosis. Advances in Dermatology and Allergology, 35, 246-250. https://doi.org/10.5114/ada.2018.74682
Balbir-Gurman, A., & Braun-Moscovici, Y. (2011). Scleroderma overlap syndrome. Israel Medicine Association Journal, 13, 14-20. PMID: 21541699
Ahmed, A., Scarborough, R., & Gabriela, R. (2018). Seronegative dermatomyositis presenting with features of anti-MDA5 subtype. Journal of Cutaneous Pathology, 45, 851-854. https://doi.org/10.1111/cup.13333
Miyachi, K., Hankins, R. W., Mimori, T., et al. (2002). Prospective study of a systemic sclerosis/dermatomyositis overlap patient presenting with anti-Ku and anti-Ki antibodies. Modern Rheumatology, 12, 253-255. https://doi.org/10.1007/s101650200040